Here’s some good news from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration:
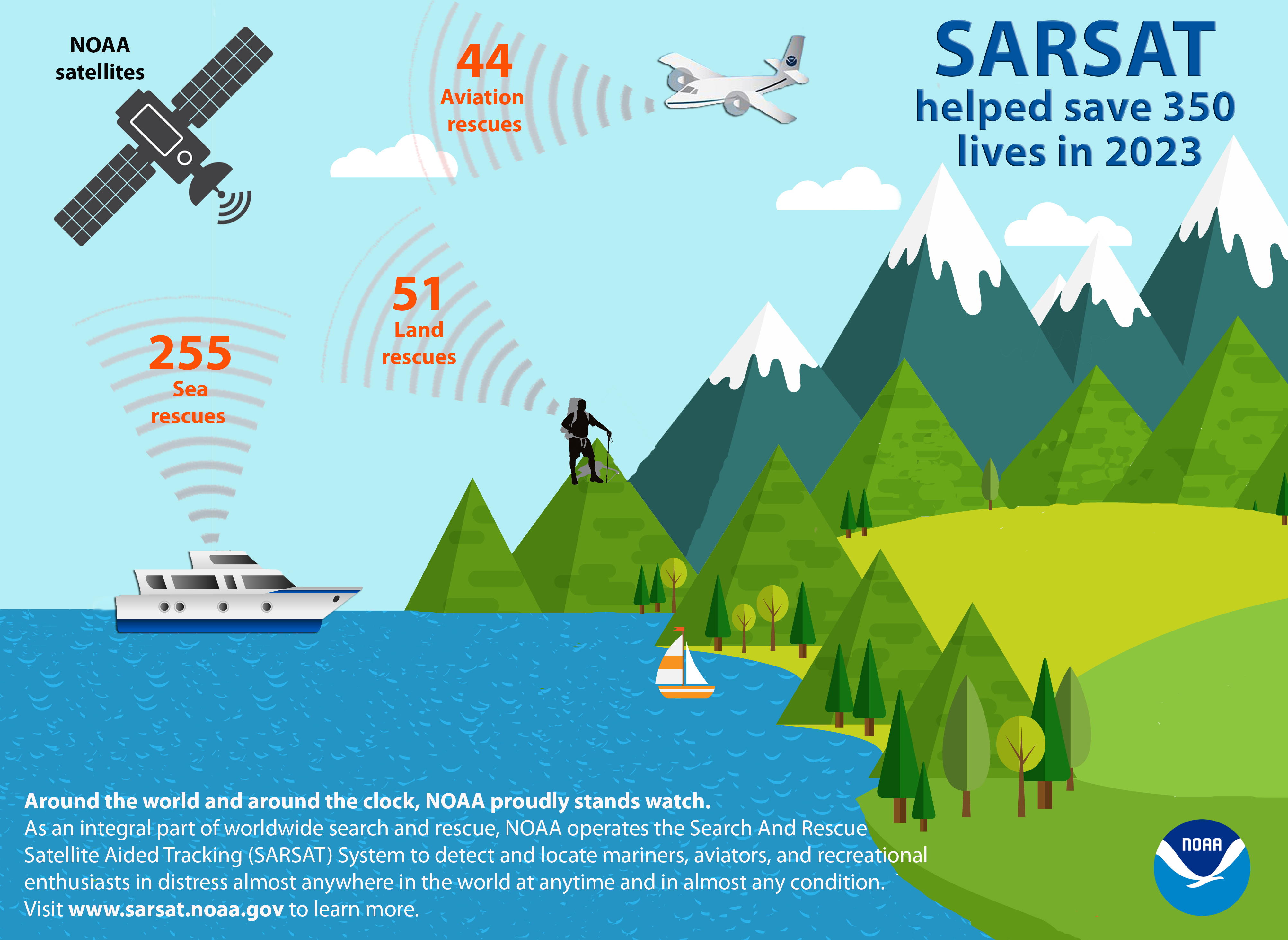
NOAA’s satellites, known for their pivotal role in tracking weather and climate, were behind the rescue of 350 people from harrowing, life-threatening ordeals in the U.S. and its surrounding waters in 2023.
NOAA’s polar-orbiting and geostationary satellites are part of the global Search and Rescue Satellite Aided Tracking system, or COSPAS-SARSAT, which uses a network of U.S. and international spacecraft to detect and locate distress signals sent from 406MHz emergency beacons onboard aircraft, boats and handheld Personal Locator Beacons (PLBs) anywhere in the world. Since its start in 1982, COSPAS-SARSAT has been credited with supporting more than 48,000 rescues worldwide, including more than 10,455 throughout the U.S. and the waters that surround it.
Of the 350 U.S. rescues last year, 255 people were pulled from the water, 44 were saved from aviation incidents and 51 were rescued on land, where PLBs were used. The record one-year total for SARSAT rescues in the U.S. stands at 421 in 2019.
When a NOAA satellite pinpoints the location of a distress signal in the U.S., the information is relayed to the SARSAT Mission Control Center at NOAA’s Satellite Operations Facility in Suitland, Maryland. From there, the information is quickly sent to Rescue Coordination Centers, operated either by the U.S. Air Force for land rescues, or the U.S. Coast Guard (USGC) for maritime rescues. NOAA also supports rescues globally by relaying distress signal information to international COSPAS-SARSAT partners.
Florida had the most people rescued with 83, followed by Hawaii with 52 and Alaska with 49.
Here’s a glimpse at three notable rescues from 2023:
- On June 12, just south of Gulf Shores, Alabama, the USGC rescued nine people from a fishing boat after its engines lost power. The crew activated the onboard beacon, which provided the location of the stranded vessel.
- On September 5, a mid-air collision between a helicopter and an aircraft resulted in minor injuries to seven passengers. The Alaska Rescue Coordination Center received the coordinates from an onboard Emergency Locator Transmitter and correlated the position to a collision report provided by the Federal Aviation Administration. The Alaska National Guard arrived on the scene to treat the passengers.
- On September 14, two people on a hike in Kukuihaele, Hawaii, fell into a ravine and were disabled. The USGC detected the distress signal from their PLB and alerted the Hawaii County Fire Department. The department dispatched a helicopter, which airlifted the hikers to a nearby hospital.
Read more at: https://www.noaa.gov/news-release/noaa-satellites-helped-save-350-lives-in-2023




